Keresés
Loire castles in France - Francia kastélyok a Loire mentén
• Château d'Angers
• Château d'Apremont
• Château d'Azay-le-Ferron
• Château d'Azay-le-Rideau
• Château de Beauregard
• Château de Blois
• Château de Bouges
• Château de la Bourdaisière
• Château de Brézé
• Château de Chambord
• Château d'Amboise
• Château de Goulaine
• Château du Lude
• Château de Châteaudun
• Château de Chaumont
• Château de Chenonceau
• Château de Cheverny
• Château de Chinon
• Château de Clermont
• Château des ducs de Bretagne
• Château de Langeais
• Château de Loches
• Château de Menars
• Château de Montsoreau
• Château du Plessis-Bourré
• Château de Plessis-lez-Tours
• Château du Rivau
• Château de Rochecotte
• Château de Saumur
• Château de Serrant
• Château de Sully-sur-Loire
• Château de Talcy
• Château de Troussay
• Château d'Ussé
• Château de Valençay
• Château de Villandry
|
Chateau d'Angers Angers kastély |
|||||||
 photo: Tango7174 photo: Tango7174 |
|
||||||
|
The Château d'Angers is a castle in the city of Angers in the Loire Valley, in the département of Maine-et-Loire, in France. It is located on a rocky ridge overhanging the river Maine. Now open to the public. the Château d'Angers is home of the Apocalypse Tapestry. Originally, this castle was built as a fortress at one of the sites inhabited by the Romans because of its strategic defensive location. In the 9th century, the Bishop of Angers gave the Counts of Anjou permission to build a castle in Angers and was expanded to its current size int he 13th century. The castle is home of the largest and oldest colletion of medieval tapesries int he world from the 14th century „Apocalypse Tapestry” by the painter Hennequin de Bruges and the Parisian tapestry-weaver Nicolas Bataille. A military academy was established in the castle to train young officers in the strategies of war.The best known cadet was Napoleon Bonaparte at the Battle of Waterloo, who was trained at the Military Academy of Angers. Still a part of the French military, the chateau was severely damaged during World War II by the Nazis when an ammunition storage dump inside the castle exploded. On January 10, 2009, the castle suffered severe damage from an accidental fire due to short-circuiting and resulting in 400 square metres (4,300 sq ft) of the roof being completely burnt. The Tapestries of the Apocalypse were not damaged. Total damages have been estimated at 2 million Euros. According to Christine Albanel, the Minister of Culture, the expected date of completion for the restoration is the second trimester of 2009. Today, owned by the City of Angers, the massive, austere castle has been converted to a museum. /Source: Wikipedia/ |
|||||||
|
A Loire- völgyi kastélyok egyike: Anger (Chateau d’Angers). Ez az erődkastély Anger városában található. Eredetileg római erődnek épült határvédelmi célok miatt, majd a 9. században Anger érseke adományozta az Anjou grófságnak. Az erődöt a 13. században építették. Az épületet egy sziklára építették, mely a Maine folyóra néz. Az erőd katonai akadémiaként is működött, melynek egyik leghíresebb kadétja a későbbi waterloo-i legyőzőtt, Napoleon Bonaparte volt. A II. világháború alatt a nácik rezidenciája lett és komoly sérülést szenvedett a lőszerraktár felrobbanása miatt. 2009. január 10-én egy váratlanul keletkezett tűzbaleset alatt több, mint 400 négyzetméteres terület és a tetőszerkezete teljesen leégett, de a francia kulturális miniszter, Christine Albanel, támogatásával hamarosan helyreállították az épületet. Ma Anger város tulajdona és a közönség előtt látogatható. Legjelentősebb kiállított mű a kastélyban az 1373 –ban Hennequin de Bruges és a párizsi goblein szövő, Nicolas Bataille által készített Apokalipszis Goblein. back |
|||||||
|
Chateau d'Apremont Apremont-kastély |
|||||||
 photo: Magali Guérineau photo: Magali Guérineau |
|||||||
|
The Château d'Apremont is a ruined 16th century château in the commune of Apremont in the Vendée département of France.It was constructed on a promontory overlooking the valley of the Vie. Portions of it are believed to date from the 13th century.[citation needed] The two extant towers were built by Philippe Chabot de Brion in the first half of the 16th century.This château is one of approximately 300 châteaux of the Loire Valley tour.The Château d'Apremont is the property of the commune. It has been listed since 1926 as a monument historique by the French Ministry of Culture. Forrás/Source: wikipedia |
|||||||
|
Chateau d’Apremont egy 16. századi romkastély Apremontban, mely a Vie völgyére néz a Vendee tartományban. Az épületnek vannak a 13. században épített részei is, de két tornya Philippe Chabot de Brion tervei alapján a 16. sz. közepén készült. 300 kastély van a Loire mentén. A Chateau d’Apremont a Municipal önkormányzat birtokában van és látogatható. Szép kilátás nyílik a keleti toronyból a Vie folyó völgyére. A kastély 1926-tól szerepel a Francia Kulturális Minisztérium listáján, a történelmi emlékművek között. back |
|||||||
|
Chateau d'Azay le Ferron Azay le Ferron-kastély |
|||||||
 photo: Guillaume photo: Guillaume |
|||||||
|
The castle of AZAY-le-FERRON looks like a typical example of the beautiful Loire castles. The castle consists of four parts built at various times: the tower Frotier (end of 15th century), the wing of Humières (middle of 17th century), the house of François I (16th century), and the Breteuil house (18th century). Several great families were owners of AZAY-le-FERRON, in particular Gregoire Michel, banker for Napoleon’s armies, later in the 19th century the castle was sold in life annuity to the Luzarche family,and his daughter bequeathed the castle and the grounds to the town of Tours in 1950. The castle is opened for the public now! It has a marvelously French and Englis style park, rose and vine, vegetable, orhard garden too. Inside the castle contains a rich furnishing exhibition and hunted stuffed animal collection. |
|||||||
|
Az épületegyüttes a Loire menti kastélyok egyik gyönyörű példája, mely Azay –le – Ferronban, a Touraine tartományban található Brenne szélén. Négy különböző időszakra tehető az építése. A Frotier torony a 15.sz. végén, a Humiéres szárny a 17. sz. közepén, az I Francois szárny a 16. században, és a Breteuil ház a 18. században épült. Különböző nagy múltú családok tulajdonában volt, mint Voltaire egyik szeretőjének az apjáé (Louis-Nicolas Le Tonnelier de Breteuil), vagy Napoleon hadseregének bankára (Gregoire Michel ) és a Luzarche család, akinek lánya 1950-ben a városnak adományozta a kastélyt. A legkiemelkedőbb látnivalója az angol és francia stílusban megtervezett parkja, a 17. századból származó rózsakertje, szőlő és gyümölcskertje. Érdekessége a belső gazdag bútorgyűjteménye különböző stílusban és afrikai vadásztrófeái. back |
|||||||
|
Chateau d'Azay le Rideau Azay le Rideau-kastély |
|||||||
 Jean-Christophe BENOIST Jean-Christophe BENOIST |
|||||||
| The castle remained in ruins until 1518, when the land was acquired by Gilles Berthelot, the Mayor of Tours and Treasurer-General of the King's finances. Desiring a residence to reflect his wealth and status, Berthelot set about reconstructing the building in a way that would incorporate its medieval past alongside the latest architectural styles of the Italian renaissance. Louis XIV, and it was during their ownership that the new château received its first royal visit: on June 27, 1619, while on his way from Paris to visit his mother, Marie de Medici, in Blois, Louis XIII broke his journey to spend the night in Azay-le-Rideau. Later in the century, his son Louis XIV would also be a guest in the same room.[ The current gardens were designed in the 19th century by the Biencourts, who created a large landscaped park in the English style. Inside many of these rooms display 16th and 17th century Flemish tapestries and significant collection of artwork as portraits of the French monachy. The building was sold 250.000 francs for the state and it is also forms part of the Loire valley UNESCO World Heritage Site. | |||||||
|
A kései reneszánsz stílusú kastély építtetője Gilles de Berthelot, I. Ferenc kincstárnoka, Tours polgármestere. A kastély helyén álló középkori várromokat 1518 környékén örökölte Berthelot felesége, Philippe Lesbahy. Az építő nevét nem ismerjük, az építkezéseket az asszony irányította. Berthelot-ot sikkasztással vádolták és még a kastély 1529-es befejezése előtt menekülnie kellett a kastélyból, melyet I. Ferenc lefoglaltatott. A kastély helyén eredetileg egy 12. századi erőd állt, mely leégett. A kastélyban több királyi utas is megfordult, többek között maga XIV. Lajos is. Az épületet egy gyönyörű angol park övezi, belül az olasz reneszánszt képviseli számos holland goblein művel és festmény gyűjteménnyel. A kastélyt 1905-ban 250.000 frankért adták el a francia államnak és ma már az UNESCO része. A közönség előtt nyitva áll, látogatható. back |
|||||||
|
Chateau de Beauregard Beauregard-kastély |
|||||||
 Photo: Manfred Heyde Photo: Manfred Heyde |
|||||||
|
The Château de Beauregard is a Renaissance castle in the Loire Valley in France. It is located closed to south of the city of Blois. Although still inhabited, it can be visited by tourists. The castle is renowned for its Gallery of portraits decorated in the 17th century with 327 portraits of famous people from France and Europe. Most of the château was built around 1545, when it was bought by Jean du Thiers, Lord of Menars, and Secretary of State to Henri II. The gallery of portraits (Galeries des Illustres in French), the largest in Europe to have survived to our days, is the masterpiece of the castle. its walls are decorated with 327 portraits of famous people having lived between 1328 and 1643 including queens, ministers, marshals, diplomats etc. The ceiling covered by the one the most expensive mineral stones from the 17th century. Also it has the biggest rose garden in Loire valley with 107 kind of roses. The castle is opened for the public. |
|||||||
|
A reneszánsz kastély néhány km-re található Bloistól. 1545-ben épült, II. Henri király titkárának, Jean de Theirs-nek. A kastély híres a felbecsülhetetlen értékű festményeiről. A gyűjtemény 327 festményt tartalmaz, egészen 1328-tól 1643- ig magába foglalva nem csak a francia, hanem az európai történelem nagyjait, királyokat, királynőket, hadvezéreket és minisztereket. A „Nagy Galéria” ma már modern kortárs művészek alkotásait is kiállítja a közönségnek. Mennyezetét az egyik legdrágább ásványi kővel borították be a 17. században. A legnagyobb rózsakerttel rendelkezik a Loire mentén, 107 fajta rózsával. A kastély látogatható. back |
|||||||
|
Chateau de Blois Blois-kastély |
|||||||
|
Photo: Tango7174 |
|||||||
|
Built in the middle of the town that it effectively controlled, the château of Blois comprises several buildings constructed from the 13th to the 17th century around the main courtyard. It has 564 rooms and 75 staircases although only 23 were used frequently. It is called as the seven kings and ten queens of French castle. It became the favourite royal residence and the political capital of the kingdom under Charles' son, King Louis XII. At the beginning of the 16th century. Although the style is principally Gothic, as the profiles of mouldings, the lobed arches and the pinnacles attest, there are elements of Renaissance architecture present, such as a small chandelier. In 1635 there was another attempt to develop the castle but on Gaston's death in 1660, it was abandoned. The château was turned into a museum. On view for visitors are the supposed poison cabinets of Catherine de' Medici. Most likely this room, the "chamber of secrets", had a much more banal purpose: exhibiting precious objects for guests.Today, the château is owned by the town of Blois and is a tourist attraction. |
|||||||
|
Itt született a későbbi XII. Lajos francia király, aki uralkodása alatt királyi rezidenciává alakítatta át Blois várát a 15. század végén gótikus stílusban. I. Ferenc, reneszánsz uralkodó, akinek egy időben Blois vára volt a legkedvesebb tartózkodási helye, reneszánsz palotát emelt az udvar másik szárnyában, s ezt jóval később egy klasszicista palotával zárta le Gaston d’Orléans, XIII. Lajos öccse. Az épületben különleges történelmi szereppel bíró helységek vannak. Pl . itt van Medici Katalin szobája, ahol 1589 januárjában elhunyt, és I. Ferenc dolgozószobája is, amelyben a gazdagon faragott faburkolat titkos fiókokat rejt, illetve a kastélyban van az a nagyterem is, ahol a rendi gyűlés ülésezett. A hét francia király és tíz királyné palotájának is nevezik, 564 szoba található benne. A kastély ma múzeum, amiben 35 ezer művészeti alkotás tekinthető meg. back |
|||||||
|
Chateau de Bouges Bouges-kastély |
|||||||
 photo: SiefkinDR photo: SiefkinDR |
|||||||
|
The château was built in 1765a and was modeled after the Petit Trianon at the Palace of Versailles. In 1818, the château became the property of Charles-Maurice de Talleyrand-Périgord, the former foreign minister of Napoleon Bonaparte. It is classified as a monument historique and the gardens are listed by the Ministry of Culture as among the Notable Gardens of France. The château and gardens are open to the public.The château and the park were location scenes in the film Le Colonel Chabert with Gérard Depardieu and Fanny Ardant. The château has a park of eighty hectares, which include a landscape garden, an arboretum, a floral garden created in 1920, large greenhouses, and a formal French garden. |
|||||||
|
A kastély 1765-ben épült a kis Trianon mintájára, mely Versailles-ban található. Több tulajdonosa közül egyik kiemelkedő történelmi személyiség 1818-ban Bonaparte Napoleon külügyminisztere volt. Kastély látogatható, illetve a Francia Kulturális Minisztérium védnöksége alatt áll figyelemre méltó kertjével együtt. Az épület filmforgatás helyszíne is volt Gérard Depardieu-vel és Fanny Ardanttal a „Colonel Chabert”-ben. A 80 hektáros kertjében gyönyörű arborétum és üvegház található, melyet 1920-ban telepítettek. back |
|||||||
|
Château de la Bourdaisière Bourdaisière-kastély |
|||||||
 Photo: Manu Photo: Manu |
|||||||
| Its origins date back to the 14th century when it was a fortress belonging to Jean Meingre. Over the next few generations, the property changed hands several time, until 1520 when King Francis I arranged for construction of a new castle on the site.Lying in ruins, in 1786 the land was sold to Louise Adélaïde of Penthièvre Bourbon. In 1802 the property was acquired by Baron Joseph Angelier who undertook a massive reconstruction of Château Bourdaisière. The interior work would be completed by his son, Gustave Angelier. Although a small château, when compared to the great châteaux of the Kings and some of those built by other wealthy nobles, it is a magnificent Renaissance construction fronted by traditional French gardens. The Castle was sold in 1923 to a wealthy American, Mrs. de Mérinville who sold it in 1938. During World War II, the château was occupied by the Nazis. After the war, a lack of funds by its owner saw it become severely run down. In 1959, its contents were auctioned off and government turned the château into a home for the elderly. It was sold again in 1988 to an attorney, François Michaud, who owned it until 1991 when it was acquired by its current owners, the Princes of Broglie who undertook significant improvements and modernization. In 2003, Château de la Bourdaisière gained considerable attention in North America, as the primary site for the television show Joe Millionaire. In 2011, the chateaus gardens were finalist for the European Garden Award bestowed by the European Garden Heritage Network The château was listed as a monument historique in 1947. (Wiki) | |||||||
| (A kastély története a 14. században kezdődik. ) A kastély 1786-ban még romos volt, felújítását báró Joseph Angelier új tulajdonos 1802-ben kezdte meg. Az eredmény egy csodálatos reneszánsz kastély lett, hagyományos francia kertekkel. A legnagyobb változás 1959-ben történt, amikor az egykori tulajdonos eladta a francia államnak és az épület idősek otthona lett egészen 1988-ig, amikor újra magánkézbe került. A kastély ma hotelként működik,és 2011-ben elnyerte az európai kertek címet, amely a legszebb kertnek járó díjat jelenti (European Garden Award bestowed by the European Garden Heritage Network). A kastély 1947-től a műemlékvédelmi listán szerepel. back | |||||||
|
Château de Brézé Brézé-kastély |
|||||||
 photo: ManuD photo: ManuD |
|||||||
| The château was transformed during the 16th and the 19th centuries. The current structure is Renaissance in style yet retains medieval elements including a drawbridge and a 12th century trogloditic basement. Today, it is the residence of descendants of the ancient lords. The château is a listed ancient monument originally dating from 1060. A range of wines are produced at the château which has 30 hectares of vineyards. (Wiki) | |||||||
| A kastély a 16. századtól a 19. századig folyamatosan épült és változott. Jelenlegi stílusát a reneszánsz jellemzi középkori elemekkel , beleértve egy felvonóhidat és egy 12. századból származó alagsor rendszert is. Ma az ősi lordok leszármazottjainak a rezidenciája és az ősi műemlékek közé sorolták a műemlékvédelem által. A kastélynak 30 hektáros szőlőültetvénye van, ahol bort termelnek. back | |||||||
|
Château de Chambord Chambord-kastély |
|||||||
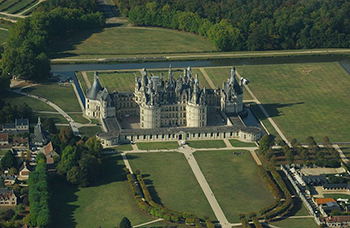 Photo: Lieven Smits Photo: Lieven Smits |
|||||||
| The royal Château de Chambord at Chambord is one of the most recognizable châteaux in the world because of its very distinct French Renaissance architecture which blends traditional French medieval forms with classical Renaissance structures.Chambord is the largest château in the Loire Valley ; it was built to serve as a hunting lodge for François I. . The original design of the Château de Chambord is attributed, though with several doubts, to Domenico da Cortona. Leonardo Da Vinci designed a central planning and double helical staircases. During the Second World War art works from the collections of the Louvre and Compiègne were moved to Château de Chambord. Now open to the public, in 2007 the château received 700,000 visitors. It is part of the UNESCO. (Wiki) | |||||||
| Chambord az egyik leghíresebb Loire-völgyi kastély, mely folyó az UNESCO világörökség része. Chambord a legnagyobb és a leglenyűgözőbb kastély a francia reneszánsz korából francia középkori elemekkel. Eredetileg vadászkastélynak építette I. Ferenc francia király. Egy hatalmas nemzeti park övezi, melyet egy I. Ferenc korabeli 32 km-es fal vesz körül. A Párizs nagyságú nemzeti park különleges növényi- és állati fajokban is gazdag. Az eredeti épület tervezése feltehetőleg Domenico da Cortonának tulajdonítható. Leonardo da Vinci építészeti újítása a dupla csigalépcső, amin úgy közlekedhetnek az emberek mindkét irányba, hogy nem ütköznek egymással össze . A második világháborúban a Louvre értékeit ide költöztették át. A kastély látogatható. Nyitvatartás: az év minden napján nyitva, kivéve január 1., november 11. és december 25. back |
|||||||
|
Chateau d'Amboise Amboise-kastély |
|||||||
 photo:Gilbert Bochenek photo:Gilbert Bochenek |
|||||||
| The royal Château at Amboise is a château located in Amboise. Confiscated by the monarchy in the 15th century, it became a favoured royal residence by Lousis XI the king and was extensively rebuilt in 1492 in Gothic style. and laterwas rebuilt again by Francis I. king in renaissance style. It has been recognised as a monument historique by the French Ministry of Culture since 1840. The chapel of Saint-Hubert where Leonardo da Vinci is buried. As a guest of the King, Leonardo da Vinci came to Château Amboise in December 1515 because the king invited him, and lived and worked in the nearby Clos Lucé, connected to the château by an underground passage. The castle is open to the public. (Wiki) | |||||||
| Amboise kastélya a 15. században került királyi tulajdonba, amikor VII. Károly elvette az Amboise grófoktól. Itt lakott XI. Lajos, mielőtt felépítette Plessis-lés-Tours-i kastélyát, majd a kastélyba költözött XI. Lajos felesége, Charlotte de Savoie és itt született 1470-ben fia, VIII. Károly,akinek kedvelt tartózkodási helye volt a kastély. VIII. Károly 1494-es olaszországi hadjárata során megismerkedett a reneszánsz stílussal. Itáliai mesterembereket hozatott a városba és a kastélyt az olasz minta szerint átalakították és berendezték. 1498. április 7-én, az új kastély felavatásakor VIII. Károly a ’jeu de pomme’ elnevezésű játékot indult megnézni. A király nem hajtotta le a fejét, homlokát beütötte a szemöldökfába, kómába esett és még aznap meghalt. Ezután unokaöccse, XII. Lajos, egy házassági szerződés értelmében feleségül vette az özvegy királynét, Anne de Bretagne-t. A kastélyt átengedte Louise de Savoi-nak, I. Ferenc anyjának. 1515-ben lépett trónra I. Ferenc, akinek uralkodása alatt élte virágkorát a város. A király folytatta az épület átépítését. Itáliai hadjárata idején nagyon megkedvelte a reneszánsz művészetet, ezért 1516-ban meghívta udvarába a 64 éves Leonardo da Vincit és neki adományozta Clos Lucé udvarházát. Leonardo Firenzéből magával vitte Franciaországba 3 festményét, ezek között volt a Mona Lisa is. Ezért található a híres festmény ma a párizsi Louvre-ban. Leonardo 3 évig, 1519-es haláláig élt Clos Lucéban. A mestert a kastély Szent Hubertus kápolnájában helyezték örök nyugalomra. |
|||||||
|
Château de Goulaine Goulaine-kastély |
|||||||
 Photo: Pymouss Photo: Pymouss |
|||||||
| For over a 1000 years, the castle has been linked to the Goulaine Family, bearing the same name.The former castle was a fortress during the middle-Age then under the Renaissance period it was entirely rebuilt in lime stone in the style of the great homes of the Loire valley. Château de Goulaine is also the estate-bottled wine produced at the château. The ownership of the Goulaine family had a break between 1788 and 1858 then they reacquired the estate and maintains it today too.The estate of Château de Goulaine has been producing wine makes it the oldest known wine business still in existence; It is believed to be the third oldest commercial enterprise in the world. It is considered the oldest European family owned business. The castle estate is one of the last Châteaux de la Loire to still be producing wine. The castle organize different kind of events, concerts, exhibitions, also they have a tropical butterfly farm.The castle is open to the public. ( http://chateau.goulaine.online.fr/index-us.html ) | |||||||
| A kastély több mint 1000 éve a de Gouaine család tulajdonában van, melyet még a 12. században szereztek meg és csak 1788 -1858 között volt más tulajdonában. 1858-ban visszaszerezték és azóta is ők a tulajdonosai. A középkorban erődként használt kastélyt a reneszánsz időben mészkőből újra építették. Legrégebbi családi vállalkozás Európában és a harmadik legrégebbi bortermelő kastély, melyet borértékesítéssel foglalkozik a mai napig. A kastély számos kulturális eseményt szervez évről-évre, illetve híres egzotikus lepke gyűjteményéről is. A kastély látogatható! (Forrás: http://chateau.goulaine.online.fr/index-us.html ) back | |||||||
|
Château du Lude Lude-kastély |
|||||||
 Photo: Manfred Heyde Photo: Manfred Heyde |
|||||||
|
The original fortress was built between the 10th and 11th centuries on the banks of the river.Louis XI's chamberlain, Jehan de Daillon, took possession of the Lude estates at the end of the 15th century. He employed Italian artists to convert the fortress into a renaissance residence. In 1751, Le Lude became the property of Joseph Duvelaër, head of the Council of The East India Company that is why it got some Chinese art style too. It has many reconstraction and there was built the classical wing in the style too. Le Lude has been passed down to the current occupants Count and Countess Louis-Jean de Nicolaÿ, who have carried on its tradition of restoration and decoration also they hold many festivals during the year to invite tourist here. It is open to the public! (http://www.lelude.com/en/chateau-du-lude.php. (Wiki) |
|||||||
| Az eredeti középkori kastély a 10-11. században épült a Loir folyó partján. XI. Lajos kamarása Jehan de Dailon vette át a 15. században, aki olasz mesterekkel komfortos és élhető reneszánsz kastélyt alakított ki. 1751-ben a francia Kelet- Indiai Társaság egyik vezetőjének Joseph Duvalier tulajdonába került, emiatt kínai stílusú jegyek is felfedezhetők. Több átépítésen esett át, ezért egyik szárnya klasszicista stílusú. A kastély mai tulajdonosa, Louis-Jean de Nicolaÿ gróf próbálja tovább vinni a tradíciókat, elsősorban különböző fesztiválokkal csalogatják ide a turistákat. A kastély látogatható! back | |||||||
|
Château de Châteaudun Châteaudun-kastély |
|||||||
 photo: Patrick GIRAUD photo: Patrick GIRAUD |
|||||||
| The castle was built between the 12th and 16th centuries in more steps and in more styles like gothic and Renaissance. The Count of Blois Thibaut V had the keep built around 1170. The bell tower was erected in 1493. Renovated since the 1930s, the castle has been classed as a historic monument (monument historique) since 1918. It’s opened to the public! (Wiki) | |||||||
| A kastély a 12. és 16.század között épült gótikus és reneszánsz stílusban több részletben, melyet először Blois Thibaut gróf kezdett meg 1170-ben. Harangtorony az 1493-as évre tehető. A kastélyt 1930-ban felújították és 1918 óta szerepel a francia műemlékvédelem listáján. A kastély látogatható. back | |||||||
|
Château de Chaumont Chaumont-kastély |
|||||||
 photo:Patrick GIRAUD photo:Patrick GIRAUD |
|||||||
| Pierre d'Amboise unsuccessfully rebelled against King Louis XI and his property was confiscated, and the castle was dismantled on royal order in 1465.[3] It was later rebuilt by Charles I d'Amboise from 1465–1475 and then finished by his son, Charles II d'Amboise de Chaumont from 1498–1510, with help from his uncle, Cardinal Georges d'Amboise; some Renaissance features were to be seen in buildings that retained their overall medieval appearance. The château was acquired by Catherine de Medici in 1560 When her husband, Henry II, died in 1559 she forced his mistress, Diane de Poitiers, to exchange Château de Chaumont for Château de Chenonceau. The castle has been classified as a Monument historique since 1840 by the French Ministry of Culture. ] Marie-Charlotte Say, heiress to the Léon Say sugar fortune, acquired Chaumont in 1875. Later that year, she married Amédée de Broglie, who commissioned the luxurious stables in 1877 to designs by Paul-Ernest Sanson, further restored the château under Sanson's direction and replanted the surrounding park in the English naturalistic landscape fashion. She donated Château de Chaumont to the government in 1938. The Château de Chaumont is currently a museum and every year hosts a Garden Festival from April to October where contemporary garden designers display their work in an English-style garden. (Wiki) | |||||||
| Eredetileg a 10. században erődként szolgált, majd később Pierre d’Amboise sikertelen király ellenes zendülése miatt XI. Lajos 1465-ban királyi rezidenciává alakította magának. Későbbiekben visszaszállt a D’Amboise családra, akik 1498-1510 között reneszánsz elemekkel díszítették a gótikus épületet. Medici Katalin 1560-ban, akinek férje II. Henri adományozta a kastélyt, halála után a király szeretőjének adta, Diane de Potitesnek, cserébe Chenonceau-ért. Az épület 1840 óta a műemlékvédelem része. 1875-ben a híres cukorgyáros Léon Say lánya, Marie-Charlotta Say és férje Amédée de Broglie vette meg a kastélyt, akik utolsó magántulajdonosként fantáziadús angol kerttel és a kastély modernizálásával fellendítették az épületet. 1938-ban a hercegnő pénzügyi gondok miatt eladta a kastélyt a francia államnak. Ma a Chaumont-sur-Loire park, művészeti és természetvédelmi központ, mely ma 32 hektáron terül el, és magában foglalja a kastélyt a környező parkot és a Nemzetközi Kertfesztivált. A kastély látogatható! back | |||||||
|
Château de Chenonceau Chenonceau-kastély |
|||||||
 WikiImage:Chateau_de_Chenonceau_2008.jpg It is a derivative work of Ra-smit's photo. WikiImage:Chateau_de_Chenonceau_2008.jpg It is a derivative work of Ra-smit's photo. |
|||||||
| The château was built on the site of an old mill on the River Cher, sometime before its first mention in writing in the 11th century. It was designed by the French Renaissance architect Philibert de l'Orme. Bohier destroyed the castle, though its 15th-century keep was left standing, and built an entirely new residence between 1515 and 1521. The work was sometimes overseen by his wife Katherine Briçonnet. Later Henry II offered the château as a gift to his mistress, Diane de Poitiers, who became fervently attached to the château along the river. However, after King Henry II died in 1559, his strong-willed widow and regent Catherine de' Medici forced Diane to exchange it for the Château Chaumont.[4] Queen Catherine then made Chenonceau her own favorite residence, adding a new series of gardens. On Catherine's death in 1589 the château went to her daughter-in-law, Louise de Lorraine-Vaudémont, wife of King Henry III. After that, it was owned by Louise's heir César of Vendôme and his wife, Françoise of Lorraine, Duchess of Vendôme. and passed quietly down the Valois line of inheritance, alternately inhabited and abandoned for more than a hundred years.Château de Chenonceau was bought by the Duke of Bourbon in 1720. Little by little, he sold off all of the castle's contents. Many of the fine statues ended up at Versailles. The estate itself was finally sold for 130,000 livres in 1733 to a wealthy squire named Claude Dupin. Claude's wife Madame Louise Dupin, brought life back to the castle by entertaining the leaders of The Enlightenment: Voltaire, Montesquieu, Buffon, Bernard le Bovier de Fontenelle, Pierre de Marivaux, and Jean-Jacques Rousseau. n 1864 Madame Pelouze bought the castle and modernized it with gaslights and costed a lot for the building. Château de Chenonceau and its gardens are open to the public. Other than the Royal Palace of Versailles, Chenonceau is the most visited château in France. The château is classified as a Monument historique since 1840 by the French Ministry of Culture. Today, Chenonceau is a major tourist attraction and in 2007 received around 800,000 visitors. |
|||||||
| Chenonceau a Loire vidékének második leglátogatottabb reneszánsz kastélya nem a Loire, hanem annak egyik mellékfolyója, a Cher mentén található. „Hat hölgy kastélyának” is szokták nevezni ezt a maga nemében egyedülálló építményt. Tervezője Philibert de l'Orme. Az első hölgy mindjárt az építtető, Catherine Briconnet, akinek 1512-ben került tulajdonába a terület. Az építkezést feleségére bízta. Bohier és felesége halála után a kincstár tette rá a kezét a kastélyra, Bohier tartozása fejében. II. Henrik a királyi kegyencnőnek, Diane de Poitiers-nek adta. Ő építtette a folyó felett a hidat, s nagy pénzért csodás kertet alakíttatott ki a kastély bejárata előtt. Amikor Henriket egy lovagi tornán halálos baleset érte, felesége Medici Katalin azonnal elkobozta a kastélyt a kegyencnőtől, cserébe neki adta Chaumont . A negyedik nő a kastély történetében III. Henrik özvegye, Louise de Lorraine volt. A kastély azután sok kézen ment át, míg a XVIII. században Dupin tábornok birtokába került. Az elegáns és művelt Madame Dupin az ötödik hölgy a kastély hányatatott történetében, a kor szinte minden jelentős művésze, írója megfordult nála. A hatodik hölgy, Madame Pelouze 1864-ben vette meg az akkor már meglehetősen elhanyagolt épületet, hatalmas összegeket áldozott rendbehozatalára, amit a kor divatjának megfelelően végeztek el. A későbbi tulajdonosok nem kis erőfeszítése révén sikerült visszaállítani az eredeti állapotot az épület nagy részén. Napjainkban, a kastély magántulajdonban van, de látogatható, berendezését a műemlékvédelem közreműködésével alakították ki. A kastély parkjában van egy viaszmúzeum, amely a kastély múltjának nevezetes szereplőit mutatja be. Évente 800 ezer látogatója van. back | |||||||
|
Château de Cheverny Cheverny-kastély |
|||||||
 photo: Jean-Christophe BENOIST photo: Jean-Christophe BENOIST |
|||||||
| It was donated by King Henri II to his mistress Diane de Poitiers. However, she preferred Château de Chenonceau and sold the property to the former owner's son, Philippe Hurault, who built the château between 1624 and 1630, to designs by the sculptor-architect of Blois, Jacques Bougier, who was trained in the atelier of Salomon de Brosse, and whose design at Cheverny recalls features of the Palais du Luxembourg. The interiors were completed by the daughter of Henri Hurault and Marguerite, marquise de Montglas, by 1650. This family has been owned the castle for 6 centuries. In 1914, the owner opened the château to the public, one of the first to do so. The family still operates it, and Château Cheverny remains a top tourist attraction to this day, renowned for magnificent interiors and its collection of furniture, tapestries, and objets d'art. A pack of some seventy dogs are also kept on the grounds and are taken out for hunts twice weekly. | |||||||
| A kastély II. Henrik szeretőjé Diane de Poitiersé volt, de ő jobban szerette volna a Chenonceau-i kastélyt, ezért eladta az előző tulajdonos fiának, Philippe Huraultnak, akinek apja 1624 és 1630 között építtette fel az épületet. Az építész az a Jacques Bougier volt, aki a Blois kastélyt is tervezte. (Jacques Bougier egyébként Salomon de Brosse a luxemburgi palota építészének tanítványa volt.) A kastély belső tereinek kialakítása Henry Hurault és lánya Marguerite, marquise de Montglas személyéhez köthetően 1650-ben lett kész. A kastély utána a Hurault család tulajdonában volt 6 évszázadon keresztül. 1914-ben ez a család volt az első, amely megnyitotta a kastélyát a látogatók előtt. Cheverny legkiemelkedőbb turisztikai attrakciói a csodálatos belső terek, valamint a bútor és enteriőr gyűjtemény, kárpitok, művészi alkotások. Turisztikai látványosság még a 70 vadászkutya, amellyel hetente kétszer vadászbemutatót rendeznek. back |
|||||||
|
Château de Chinon Chinon-kastély |
|||||||
 Photo: Franck Badaire Photo: Franck Badaire |
|||||||
| Château de Chinon was founded by Theobald I, Count of Blois. In the 11th century the castle became the property of the counts of Anjou. In 1156 Henry II of England, a member of the House of Anjou, took the castle from his brother Geoffrey after he had rebelled for a second time. Henry favoured the Château de Chinon as a residence: most of the standing structure can be attributed to his reign and he died there in 1189. Early in the 13th century the castle became under French control again.Used by Charles VII in the 15th century, On 6 March 1429 Joan of Arc arrived at Château de Chinon. She claimed to hear heavenly voices that said Charles would grant her an army to relieve the siege of Orléans.[ and Charles sent her to the army at Orleans later. | |||||||
| A kastély I. Theobald Blois grófja által lett alapítva a 10. században, majd a 11. században az Anjou-k vették a birtokukba. II. Henrik angol királynak sok bosszúságot okozott Geoffrey bátyja, aki másodszor is testvére, a király ellen fordult, ezért 1156-ban Henrik elvette a kastélyt bátyjától. Henrik egyik kedvenc rezidenciája lett a kastély, mely ekkor fejlődött a legtöbbet és nyerte el végső struktúráját. II Henrik végül egészen 1189-ben bekövetkezett haláláig itt élt. A kastély a 13. században ismét francia kézbe került. A 15. században VII. Charles uralkodó idején érkezett meg a várba 1429 március 06-án Joan of Arc, a későbbi Joan’d Arc, akit király a kérésére Orleans mellett harcba küldött. A 16. század második felétől főként börtönként használták, de később ez a funkciója megszünt, és a kastély sorsa hanyatlásnak indult. 1840-ben a Francia Kulturális Minisztérium által a francia műemlékek listájára került műemlékként. Napjainkban a Loaire menti önkormányzat és turisztikai hivatal irányításában múzeumként működik. 2003-2010 között 14,5 millió eurós támogatással egy felújításon esett át. back | |||||||
|
Château de Clermont Clermont-kastély |
|||||||
 Photo: Jibi Photo: Jibi |
|||||||
| Clermont, built between 1643 and 1649 in renessaince style. It was owned by the Maupassant family before becoming the property of the actor Louis de Funès. It was built by the Chenu de Clermont, a family of important military administrators. The Château de Clermont was built shortly after the Battle of Rocroi (19 May 1643), where the Grand Condé, saved the throne of the enfant Louis XIV and merited a considerable reward. It reflects enthusiasm of a period filled with glory. It is surrounded by 3 hectares (7.4 acres) of parkland and a vineyard of 17 hectares (42 acres). Louis de Funès had a rose garden planted, but nothing remains of it today.The wings of Clermont are very different from those of other châteaux from the same period of the 17th century. The castle is opened to the public and takes place for many festivals during the Summer. (Wiki) | |||||||
| A kastély 1643 és 1649 között épült reneszánsz stílusban. A Cheni de Clermont család által volt építtetve, akik az egyik legbefolyásosabb katonai családnak számítottak abban az időben. A Rocro csatában a Clermont családnak jelentős érdemei voltak abban, hogy, XIV. Lajos király francia király megtarhatta trónját, ezért a király hálája jeléül nekik adományozta a területet, ahol később a kastély felépült.
Majd a Maupassant család birtokában volt, mielőtt a híres színész Louis de Funés tulajdonába került. A kastélyhoz tartozik 3 hektár park és 17 hektár szőlős. A színésznek egykoron rózsakertje volt itt a kastély kertjében. A kastély látogatható, és nyáron több fesztivál helyszínéül is szolgál. back |
|||||||
|
Château des ducs de Bretagne Bretagne-kastély |
|||||||
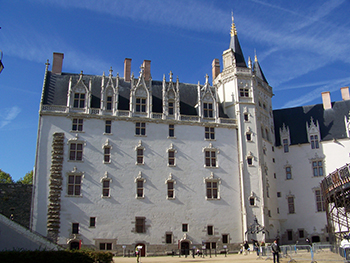 photo: Florestan photo: Florestan |
|||||||
|
The Château des ducs de Bretagne (English: Castle of the Dukes of Brittany) is a large castle and it served as the centre of the historical province of Brittany until its separation in 1941. It was the residence of the Dukes of Brittany between the 13th and 16th centuries, subsequently becoming the Breton residence of the French Monarchy. The castle's inner courtyard reveals a 15th century ducal palace built of tufa stone in the Renaissance style, together with other buildings from the 16th to the 18th centuries. The castle has been listed as a monument historique by the French Ministry of Culture since 1862. Today the castle houses the Nantes History Museum which was restored between 1990 and 2007. Now is a popular tourist attraction which includes 32 rooms and presents 850 objects of collection. The 500 metre round walk on the fortified ramparts provides views not just of the castle buildings and courtyards but also of the town. The night-lighting brings out the architectural complexity of the site within an urban context. The illumination was designed by Sylvie Sieg and Pierre Nègre of the Atelier Lumière and won the Light Originator Price of the Lumiville Trophy 2007. (Wiki) |
|||||||
|
A kastély a francia Bretagne-ban, Nantes városában helyezkedik el az Atlanti óceán partján, és egészen 1941-ig központja volt Bretagne-nak. Az épület a Bretagne grófok rezidenciája volt a 13. és 16. században, majd később a francia monarchiájé volt. A kastély belső része a 15. században készült mészkőtufából reneszánsz stílusban, más épülettel együtt a 16. és 18. században. A kastély 1862-ben a francia kulturális minisztérium által a műemlékek listájára került. Napjainkban a kastély ad otthont Nante város Történelmi Múzeumának, melyet 1990 és 2007 között felújítottak. A turisztikai látványosság 32 szobát és 850 tárgyból álló gyűjteményt foglal magában. A kastély falain 500 méteres sétány található, ahonnan gyönyörű kilátás van a városra. Az épület éjszaka ki van világítva, melyet Sylvia Sieg és Pierre Négre tervezett és elnyerte Lumiville Trófeát 2007-ban. back |
|||||||
|
Château de Langeais Langeais-kastély |
|||||||
 photo: sybarite photo: sybarite |
|||||||
| The Château de Langeais is a medieval castle which was founded in 992 by Fulk Nerra, Count of Anjou, the castle was soon attacked by Odo I, Count of Blois. After the unsuccessful attack, the now-ruined stone keep was built; it is one of the earliest datable stone examples of a keep. Between 994 and 996 the castle was besieged unsuccessfully twice more. During the conflict between the counts of Anjou and Blois, the castle changed hands several times.After it was destroyed during the Hundred Years' War, King Louis XI (1461–1483) rebuilt Château de Langeais into what today is one of the best known examples of late medieval architecture. It is especially noted for its monumental and highly decorated chimneypieces. Restored in the late 19th century, Château de Langeais came under the control of the Institut de France, who own the site today. The great hall of the château was the scene of the marriage of Anne of Brittany to King Charles VIII on December 6, 1491 that made the permanent union of Brittany and France.In 1886, Jacques Siegfried bought Château Langeais and began a restoration program. He installed an outstanding collection of tapestries and furnishings and bequeathed the château to the Institut de France which still owns it today. The château is open to the public. It is listed as a monument historique by the French Ministry of Culture. | |||||||
|
Ezt az impozáns középkori várat 992-ben alapította Fulk Nerra Anjou gróf. Az építés után hamarosan megtámadta I Odo Blois grófja. A várostrom sikertelen volt, de az erődöt újra kellett építeni. 994 – 996 között még kétszer érte nagyobb támadás a várat. A konfliktus alatt mely az Anjouk és Bloisok között alakult többször váltott tulajdonost, míg a 100 éves háború után XI. Lajos újjáépítette és a legszebb kései középkori kastéllyá emelte. Kiemelkedő építészeti elemei, a díszített kémények. A 19. században a Francia Intézet vette gondozásba, mely ma is tulajdonosa. A nagy terem pl. színhelye volt Bretagne Anne és VIII. Károly király esküvőjének 1491-ben, mely állandó unióvá kovácsolta össze Bretagnet és Franciaországot. 1886-ban egy nagy rekonstrukciós programon esett át Jacques Siegfried vezetésével. Ekkor kapta meg ma is látható kárpit és bútor gyűjteményét. A kastély látogatható! Az épület a francia minisztérum műemlékei között van nyilvántartva. back |
|||||||
|
Château de Loches Loches kastély |
|||||||
 |
|||||||
|
It was constructed in the 9th century. Built some 500 metres (1,600 ft) above the Indre River, the huge castle, famous mostly for its massive square keep, dominates the town of Loches. The castle was captured by King Philip II of France in 1204.The castle would become a favorite residence of Charles VII of France, who gave it to his mistress, Agnès Sorel, as her residence. It would be converted for use as a State prison by his son, King Louis XI.During the American Revolution, France financed and fought with the Americans against England and King Louis XVI used the castle of Loches as a prison for captured Englishmen.At the time of the French Revolution, the château was ransacked and severely damaged. Some major restoration began in 1806 but today there are parts visible as ruins only. Owned by the Commune of Loches, the castle and the adjacent ancient Church of Saint-Ours are open to the public. Château de Loches has been recognised as a monument historique since 1861 and is listed by the French Ministry of Culture. (wikipedia) |
|||||||
| A kastélyt a 9 sz.-ban építették, mely 500 méter magasan fekszik az Indre folyó felett. Fülöp francia király vette uralma alá 1204-ben, de igazán híres királyi rezidenciává VII. Károly idején vált, aki szeretőjének Agnes Sorelnek adta. Később, XI.Lajos uralma alatt állami börtönként használták, majd az amerikai forradalom kitörésekor a franciák az angolok elleni háború támogatásaként angol foglyokat tartottak itt. A francia forradalomban számos helyen megsérült, és 1806-ban el kezdték felújítani, ezért ma már csak pár jel utal az akkori romokra. Ma a loches-i önkormányzat tulajdonában áll és a szomszédos ős régi Szent Ours templommal együtt nyitva áll a látogatók előtt. 1861 óta a Francia Kulturális Minisztérium műemlékként tartja számon. back | |||||||
|
Château de Menars Menars kastély |
|||||||
 Peter Dutton from Forest Hills, Queens, USA Peter Dutton from Forest Hills, Queens, USA |
|||||||
| Towards 1646, Guillaume Charron, adviser of the King and general treasurer of extraordinary levies supplying French forces in the Thirty Years War built his chateau.In 1760, Menars was acquired by Mme de Pompadour, who paid almost 1,000,000 livres in installments and "sold some pearl bracelets to meet the first payment". The king's mistress charged the architect Ange-Jacques Gabriel with constructing two new wings on both sides of the two pavilions, which replace those built in the seventeenth century.After 1830, Joseph, prince de Caraman-Chimay established at the Château de Menars an establishment he called the "prytanée" which aims to bring together young people of different conditions and nationalities to give them a common education. Gardens : Jean-Jacques Cartwright, in the second half of the seventeenth century, arranged a formal garden then during Marigny's tenure an English garden was created in the Bois-Bas. ( Wiki) |
|||||||
| 1646 táján Guillaume Charron a királyi tanácsadó és kincstárnok építette fel a kastélyt a 30 éves háború alatt. 1760-ban Menars Madame Pompadour birtokába került, aki 1 millió lírát költött az épület tovább bővítéséért. Ange-Jacques Gabrielt építészt bízta meg, hogy alkosson 2 nagy új szárnyat mindkét irányban. 1830 után József Caraman-Chimay hercege egy iskolát alapított itt, ahol különböző társadalmi osztályból származó, illetve nemzetiségű diákokat tanítottak itt, a tolerancia, egymás elfogadása szellemében. Kertépítészete: Jean-Jacques Cartwright irányítása alatt, a 17. sz.második felében épített kertet alakítottak ki. Később Marigny angol kertté alakíttatta át, amely a Bois Bas elnevezést kapta. back |
|||||||
|
Château de Montsoreau Montsoreau kastély |
|||||||
 photo:free |
|||||||
| The Château de Montsoreau is a castle in the market town of Montsoreau. It was constructed in 1455 by Jean de Chambes, a senior councillor to King Charles VII and it was a strategic fortress, controlling river traffic. Montsoreau was directly built in the river. Alexandre Dumas's novel La Dame de Monsoreau is based upon the amorous escapades of two ladies who occupied the castle during the reign of King Henri III. By the end of the 19th century, the castle was abandoned and nearly in ruins. Today, having undergone extensive renovation, it is owned by the département and houses the Musée des Goums Marocains. So in the 20th century the castle became a museum during 50 years.The Château de Montsoreau has been listed as a monument historique by the French Ministry of Culture since 1862.The castel is opened in front of the public.( Wiki) | |||||||
| A mezővárosi Montsoreau kastélyt, 1455-ben építtette Jean de Chambes, VII. Károly király kancellárja. Az épület erődként funkcionált,és a folyón átmenő forgalmat ellenőrizte. Alexandre Dumas egyik szerelmi szálakkal átszőtt regénye a Montsoreau grófnője is itt játszódik, melyben két hölgy foglalja el a kastélyt. A történet III. Henrik király idejében játszódik. A 19. sz.-ban a vár üresen állt, majdnem romos állapotba került. Ma már teljesen rendbe hozva múzeumként működik közel 50 éve. 1862-től a Franci Kulturális Minisztérium listáján műemlékként szerepel. A kastély látogatható. back | |||||||
|
Château du Plessis-Bourré Plessis-Bourré kastély |
|||||||
 |
|||||||
| Château du Plessis-Bourré was built in less than 5 years from 1468 to 1472 by Finance Minister Jean Bourré, the principal advisor to King Louis XI. The château has not been modified externally since its construction and still has a fully working drawbridge. It was classified as a Monument historique in 1931.It is currently inhabited by descendants of François Reille-Soult of Dalmatie and managed by Aymeric d'Anthenaise and Jean-François Reille-Soult de Dalmatie. The Château du Plessis-Bourré has been the location setting for numerous films, including: Jeanne d'Arc (1989 telefilm) by Pierre Badel, Fanfan la Tulipe (2003) by Gérard Krawczyk, Louis XI, Le Pouvoir Fracassé (2010) by Henri Helman with Jacques Perrin… stb. ( Wiki) | |||||||
| Az épület 5 éven át épült 1468 és 1472 között az akkor pénzügyminiszter Jean Bourré által, aki XI. Lajos tanácsadója volt. A kastély azóta nem volt változtatva, minden az eredetiben pompázik a felvonóhíddal együtt. 1931 óta történelmi műemlékként van jegyezve. A kastélyt Aymeric d'Anthenaise and Jean-François Reille-Soult de Dalmatie igazgatja. Magánkézben van, de rengeteg filmnek adott már otthont ennek ellenére, mint pl. Jeanne d’Arce, Tulipan Fanfan, Gérard Krawczyk, XI. Lajos Le Pouvoir Fracassé (2010) Henri Helman alkotása a Jacques Perrin…stb. ( A kastélyt vizesárok veszi körül, és tipikus példája a kastély, és a várépítészet közti átmenetnek. ) back |
|||||||
|
|
|||||||
 photo: Original uploader was NonNobis at fr.wikipedia photo: Original uploader was NonNobis at fr.wikipedia |
|||||||
| The Château de Plessis-lez-Tours is the remains of a late Gothic château located in the town of La Riche. Around three fourths of the former royal residence were pulled down during the French Revolution in 1796.Plessis-lez-Tours was the favorite residence of King Louis XI of France, who died there on 30 August 1483. The present building is only a small part of the château originally built by Louis XI in the 15th century. The room where Louis XI died can be visited. The remaining wing, which had long been used as a dairy farm and a buckshot factory, has been listed as a monument historique since 1927 by the French Ministry of Culture. ( Wiki) | |||||||
|
A kastély késő gótikus stílusban építették felmely La Riche városában található. Az eredetileg U alakú épület háromnegyed részét lerombolták a francia forradalomban 1796-ban. A kastély XI. Lajos egyik kedvenc tartózkodási helye volt és itt is halt meg 1483. aug. 30-án. Jelenleg az épületből csak kis rész látogatható, melybe beletartozik XI. Lajos szobája is, ahol elhunyt. A megmaradt szárnya az épületnek volt tejüzem, és sörgyár is. 1927 óta francia műemlékként tartják nyilván. (Előfutára a kecses lakóingatlanoknak a Loire völgyben.) back |
|||||||
|
Château du Rivau Rivau kastély |
|||||||
 |
|||||||
| The Château du Rivau is a castle-palace in Lémeré.Its shape is reminiscent of 13th century fortified castles as suggest the square layout one can still discern. Yet the Rivau was one of the first ornamental castles to be built: its cheminees, wide windows and frescos endow it with a harmonious style. The Château du Rivau is intimately linked to the illustrious Beauvau family. Le Rivau remained in the family's possession for 247 years.Humanised by the Renaissance, Le Rivau is one of the most important momuments of the Touraine region. Le Rivau listed among the Historical Monuments in 1918.The painter Pierre-Laurent Brenot lived at Le Rivau from 1960 to 1992.At the end of the 20th century, Le Rivau as though touched by a magic wand, found once again its original splendour after a 18-years restoration campaign. Today it seems to be taken directly from a book of fairytales and legends.The 12 gardens of Rivau are designated a Jardin Remarquable (by a French organisation that recognises remarkable gardens). They are inspired by fairy tales and legends and take the visitors on a beautiful and fantastical journey. | |||||||
| A kastély du Rivau Lémeré-ben található, melyet a 13. sz.-ban építettek. Az egyike az első díszes kastélyoknak, mellyet már hatalmas kéményei és széles nagy ablakai, illetve freskói harmonikus egységben jellemeznek. ( A kastély jól tükrözi a várépítészet,és a kastélyépítészet átmenetét, összekapcsolódását.) 247 éven át az illusztris Beauvau család birtokolta. A reneszánsz egyik legfontosabb építményei közé tartozik. 1918 óta francia műemlék. Pierre –Laurent Brenot egyik festő élt itt 1960 és 1992 között. A 20. sz. végén nagy restauráláson esett át és ezzel egy csodás tündérmesébe illő kertet hoztak létre mely 12 részből áll. A kastély látogatható. back |
|||||||
|
Château de Rochecotte Rochecotte kastély |
|||||||
 |
|||||||
| The château de Rochecotte is a late 18th century château located in the French village of Saint-Patrice, near Langeais. It is known for its various owners and their many successive rebuilds.Originally, the château belonged to the comte de Rochecotte. On 30 April 1828, one of the later owners, the chevalier René de La Selle de Ligné, sold it to Dorothée de Courlande, duchess of Dino, and Prince of Talleyrand, has welcomed a number of illustrious political, literary and aristocratic figures, such as Honoré de Balzac, Adolphe Thiers, or even King George IV of England and the Queen. It is surrounded by a magnificent wooded park with French gardens, an ornamental lake and a large swimming pool alongside a pathway of limetrees.Today, Rochecotte is a beautiful hotel where the relaxed way of life, so dear to the Duchess of Dino, continues to perpetuate. ( Wiki) | |||||||
|
A 18. sz.-ban épült kastély Saint-Patrice faluban található, melynek számos tulajdonosa volt és többször át lett építve. Eredetileg a Rochecotte családé volt, majd később 1828-ban az akkori tulajdonosa eladta Dino hercegnőnek és Talleyrand hercegnek. Számos híres politikus, művész, mint Honoré de Balzac, illetve arisztokrata, mint IV. Görgy angol király is megfordult itt. Ma hotelként funkcionál és gyönyörű park veszi körül francia kerttel és tóval. back |
|||||||
|
Château de Saumur Saumur-kastély |
|||||||
 photo: Kamel15 photo: Kamel15 |
|||||||
| The Château de Saumur, originally built as a castle and later developed as a château, is located in the French town of Saumur and it was originally constructed in the 10th century by Theobald I, Count of Blois, as a fortified stronghold against Norman predations. The castle was rebuilt by Henry II of England in the later 12th century. In the early part of the 13th century, Philip II of France made Saumur part of his royal domain. In 1621 the castle was converted into an army barracks. Nearly two centuries later it was converted into a state prison under Napoleon Bonaparte.In the first part of the 20th century, the city of Saumur acquired the castle and began a restoration program to house the museum of the decorative arts.The Château de Saumur has been listed as a monument historique by the French Ministry of Culture since 1862. As of 2008, there are a total of 46 buildings and structures in Saumur which are designated a Monument Historique; designed by the renowned architect Jean Drapeau, it is recognised for its light and elegant architecture. ( Wiki) | |||||||
| A Saumur városában található kastély, eredetileg várként funkcionált és csak később építették át kastélynak. Az eredetijét a 10. században I. Theobald Blois grófja építtette a normanok elleni védekezéshez. Később II. Henry angol király a 12. században átépíttette, majd a 13. századttól királyi rezidenciája volt II. Fülöp francia királynak. 1621-ben katonai létesítmény majd 2 évszázadig börtönként működik egészen Napóleon hatalomra jutásáig. A 20. század első felében egy újjászervezési program keretében művészeti múzeummá alakítják. 1862 óta a Francia Kulturális Minisztérium emlékműként tartja számon. 2008-ban ismét nagy újjáépítésen esik át a teljes 46 épület, mely Jean Drapeau építész tervezése alapján könnyed eleganciát kap. A kastély látogatható! back | |||||||
|
Château de Serrant Serrant-kastély |
|||||||
 photo: Manfred Heyde photo: Manfred Heyde |
|||||||
| The Château de Serrant is a Renaissance château was built on the foundations of a medieval fortress. From the 14th century the castle was held by the Brie family. Ownership of the castle then changed hands several times before Guillaume de Bautru, a State Councillor, purchased the property in 1636. In 1749, the estate was sold by the last surviving descendant of the de Bautru family and was bought by Antoine Walsh, a shipowner who was redecorating the interior of the castle, the Walsh family built an English style park, pavilions, and a monumental gate complete with the family crest. The château eventually passed out of the hands of the Walsh family in 1830 when Valentine Walsh de Serrant married the Duc de La Trémoïlle. The La Trémoïlle family still own the château, but in the 20th century it has been modernised with cellars and the introduction of electricity.The castle is notable for the library, stocked with 12,000 books; the vaulted halls, originally home to the kitchens; and Napoleon's bedroom, which was never used by the Emperor as he stayed at the castle for only two hours. ( Wiki) | |||||||
| A reneszánsz kastély egy középkori erőd alapjaira épült, mely a 14. századtól a Brie család birtokában volt. Számos tulajdonosai közül kiemelkedő de Bautru állami kancellár, aki 1636-ban vette meg. 1749-ben Antonie Walsh hajótulajdonos kezébe került, aki több belsőépítészeti és külső változatásokat hajtott rajta végbe, mint pl. a nagyszabású kapu, angol park, pavillonok…stb. 1830-ban házasságkötés következtében a La Trémoille családra szállt, akik a mai napig is a tulajdonosai. A 20. században korszerűsítették és bevezették az áramot. A kastély legkiemelkedőbb része a 12 ezer könyvből álló könyvtár, eredeti állapotban lévő konyha és a napoleoni hálószoba, melyet maga a császár használt csupán 2 óra hosszára. back | |||||||
|
Château de Sully-sur-Loire Sully-sur-Loire-kastély |
|||||||
 photo : GIRAUD Patrick photo : GIRAUD Patrick |
|||||||
|
The Château de Sully-sur-Loire is a castle which was built by Henri IV's minister Maximilien de Béthune (1560–1641), and the site has perhaps been fortified since Gallo-Roman times, certainly since the beginning of the eleventh century. Guy de la Trémoille, inheriting the fortress, undertook the construction of the "Donjon". The Château de Sully-sur-Loire remained in the possession of the family until 1962 when it became a property of the Département du Loiret, and has since benefited from numerous restorations. It hosts a classical music festival each June. The château contains numerous tapestries (including a set of six seventeenth-century hangings, the Tenture de Psyché), paintings of Sully's ancestors and heirs, and seventeenth-century furnishings. Later, in 1716 and again in 1719 the château sheltered Voltaire, when he had been exiled from Paris for affronting the Régent, Philippe, duc d'Orléans.Château de Sully-sur-Loire is listed as a monument historique by the French Ministry of Culture. ( Wiki) |
|||||||
| A kastély IV. Henrik minisztere Maximilien Béthune építtette 1560-1641 között, melynek egyik része feltehetően a gallo-román időkből származik a 11. századból. De la Trémoille örökölte meg, aki több átalakítást hajtott végre rajta. A család egészen 1962-ig birtokolta majd a du Loiret Hivatala vette át. A kastély számos gobleint tartalmaz a 17. századból, illetve festményeket és 17. századi bútorzatot. Több felújításon esett át és ma otthont ad a júniusi klasszikus zenei fesztiválnak. Fontos történelmi szerepet töltött be, amikor Voltaire-nek adott menedéket, aki Párizsból menekült ide, mert szembe került a régenssel. A Francia Kulturális Minisztérium műemlék listáján szerepel. back | |||||||
|
Château de Talcy Talcy-kastély |
|||||||
 |
|||||||
| It is a historical building in Talcy.It was commissioned around 1520 by Bernardo Salviati, a Florentine condottiero and cardinal with connections to the Medici family. It is more Gothic in its vernacular feeling that might be expected in a structure built for an Italian patron at the height of the Renaissance.The estate is better known in literary rather than architectural history. Salviati's daughter and granddaughter, Cassandre and Diane, were the muses of two leading French poets of the time, Pierre de Ronsard and Théodore-Agrippa d'Aubigné, respectively. Ronsard fell in love with the 15-year-old Cassandre in 1552, during his stay at Talcy. He dedicated to her some of the best known sonnets in the French language. D'Aubigné, a neighbour of the Salviati, composed for Diane in 1571 the collection of sonnets, ballads.The Salviati retained the ownership of the estate until 1682. In 1932 it was sold to the state, on condition that the 18th-century interiors would be preserved intact. The château is visited by 20,000 tourists annually. (Wiki) | |||||||
| A kastély 1520 körül lett építették Bernardo Salvati jóvoltából, aki az olasz Medici családdal volt kapcsolatban. Inkább gótikus, mint reneszánsz épület, mely elsősorban nem az építészeti stílusa miatt, hanem inkább az irodalmi háttere miatt vált híressé Franciaországban. Salvati leánya és unokája Cassandre és Diane két korabeli híres költőnek lettek a múzsái, Pierre de Ronsardé és Thodore – Agrippa d’ Aubignéjé. Mindketten szerelmesek lettek a hölgyekbe, akiknek számos verset és szonátát írtak 1552-ben és 1571-ben. A Salvati család egészen 1682-ig uralta a kastélyt. 1932-ben végül az állam vette meg, mely azóta látogatható, és több mint 20 ezer látogatót vonz évente. back | |||||||
|
Château de Troussay Troussay-kastély |
|||||||
 |
|||||||
|
This is one of the smallest Châteaux of the Loire Valley, and is situated in Cheverny, in the Loir-et-Cher. the first stone of the mansion was placed around 1450, the oldest existing parts of the structure date from the Renaissance. The owner was Robert de Bugy, director of the salt storehouses of the region of Blois. In 1732, for the first time, the building changed owners: the last demoiselle de Bugy sold the château to the Pelluys family. After passing through various owners... In 1900, the château was sold a second time to the family of the current owners, not wanting to move away from the Château de Cheverny, the owners have remained the same family. he castle being private and inhabited, only six rooms on the ground floor are open to visitors. The old French formal garden were completely abandoned in the 18th century; the park of the château had a rebirth in the 19th century. (Wiki) |
|||||||
|
A legkisebb Loire menti reneszánsz kastély Cheverny-ben, melyet 1450 körül alakítottak ki a mai formájára. A tulajdonosa Robert de Bugy az egykori sóház tulajdonosa is volt egyben a Blois régióban. A kastély fennállása történetében először 1732-ben cserélt gazdát: demoiselle de Bugy eladta a kastély a Pelluys családnak. Több tulajdonosa volt, majd 1900-ban vette meg a kastélyt ma is birtokló család. A kastélyban összesen 6 szoba látogatható. A kastély körül gyönyörű francia park volt a 18. században, melyet a 19. században felújítottak. back |
|||||||
|
Château d'Ussé d'Ussé-kastély |
|||||||
 Photo: Manfred Heyde Photo: Manfred Heyde |
|||||||
|
In the fifteenth century, the ruined castle of Ussé was purchased by Jean V de Bueil, a captain-general of Charles VII who became seigneur of Ussé in 1431 and began rebuilding it in the 1440s In the seventeenth century demolished the north range of buildings in order to open the interior court to the spectacular view over the parterre terrace, to a design ascribed to André Le Nôtre. The tradition maintained at Ussé is that this was the castle Charles Perrault had in mind when writing "The Sleeping Beauty" . Famed for its picturesque aspect, Ussé was the subject of a French railroad poster issued by the Chemin de Fer de Paris à Orléans in the 1920s] and was one of several that inspired Walt Disney in the creation of many of the Disney Castles.It is classified as a monument historique since 1931 by the French Ministry of Culture Belongs today to the de Blacas family. (Wiki) |
|||||||
| A 15.sz.-ban a romvárat VII. Károly francia király kapitánya Jean V de Bueil újjáépíttette. A munkálatok 1431-ben kezdődtek, és 1440-ben fejeződtek be. A 17. században André Le Notre által tervezett teraszt és számos új épületet kapott a kastély, illetve szépsége megihlette Charles Perraultot, akit a Csipkerózsika megírására inspirálta az épület. A kastély látványa később a francia vasútvonalának a poszterére is rákerült a Chemin de Fer de Paris á Orleans által 1920-ban, de Walt Disneyt is megfogta, aki több rajzfilmjében is felhasználta, mint Disney várat. Az épület 1931 óta műemlék. Ma a Blacas család tulajdonában van, de emellett látogatható. back |
|||||||
|
Château de Valençay Valençay-kastély |
|||||||
 Jean-Christophe BENOIST Jean-Christophe BENOIST |
|||||||
| Its architecture invites comparison with the Renaissance châteaux of the Loire Valley.The château, was built on a royal scale by the d'Estampes family of financiers over a period of some 200 years. Construction started in 1540 and was not completed until the 18th century, when the south tower was added.
The 18th century saw a rapid succession of owners, including the notorious Scottish banker John Law, who purchased the estate in 1719. Nearly a century later, in 1803, Napoleon ordered his foreign minister Charles Maurice de Talleyrand to acquire the property It is clothed in classical orders: the Doric order on the ground floor, the Ionic order on the first floor, and the Corinthian order on the second. Talleyrand's château boasts one of the most advanced interiors of the Empire style anywhere. (Wiki) |
|||||||
| A kastélyra a Loire menti reneszánsz stílus a jellemző. A kastélyt a királyi tekintélyű d’Estampes család építtette, és birtokolta is közel 200 éven át. Az építkezés 1540-ben kezdődött és a 18.sz.-ban fejeződött be, amikor a déli torony lett hozzáépítve. A 18. sz. több tulajdonosváltáson ment át a kastély, majd egy skót bankár John Law vette meg 1719-ben. 1803-ban Napóleon külügyminiszterének Cahrles Maurice de Taileyrand tulajdonába ment át. Ez volt a kastély történelmének aranykora. A család egészen 1952-ig uralta a kastélyt, amikor is megszakadt a férfi családi ág, és az utolsó herceg mostohafiára hagyta az épületet, aki eladta egy intézet részére 1979-ben. Az épületben több száz szoba látható, melynek egy negyede a Taileyrand család lakóterét mutatja be, de látható Ferdinánd király szalonja is. Szép francia parkja a korai 20. században lett tervezve nem beszélve a 40 hektáros területtel, szőlőssel, és a benne található különböző egzotikus állatokkal, mint, lámák, pávák, amelyek kellems kikapcsolódást adnak a turisták számára. A Taileyrand kastély belső építészetében megjelenik a klasszicizmus, és az empire is. back |
|||||||
|
Château de Villandry Villandry-kastély |
|||||||
 Photo: Jean-Christophe BENOIST Photo: Jean-Christophe BENOIST |
|||||||
| The lands where an ancient fortress once stood were known as Colombier until the 17th century. Acquired in the early 16th century by Jean Le Breton, France's Controller-General for War under King Francis I, a new château was constructed around the original 14th-century keep where King Philip II of France once met Richard I of England to discuss peace. During the French Revolution the property was confiscated and in the early 19th century, Emperor Napoleon acquired it for his brother Jérôme Bonaparte. In 1906, Joachim Carvallo purchased the property and poured an enormous amount of time, money and devotion into repairing it and creating what many consider to be the most beautiful gardens anywhere. (Wiki) |
|||||||
| A hely, ahol az öreg erőd állt Colombier néven volt közismert a 17.sz.-ig. A 16.sz.-ban Jean Le Breton I. Ferenc kapitánya vette meg. A 14. századi új épület azért fontos, mert itt találkozott II. Fülöp francia király I. Richárd angol királlyal, hogy békét kössenek. A francia forradalomban elkobozták, majd a 19. sz. elején Napóleon fivérének Jérome Bonapartenek adományozta. 1906-ban Joachim Carvallo tulajdonába került, aki rengeteg időt és pénzt áldozott rá. Ekkor készült el gyönyörű kertje. 1934-ben műemlékké nyilvánították és a világörökség részévé vált. Ma továbbra is a Carvallo család tulajdona, de látogatható. back | |||||||
|
|
|||||||
